Abstract
Introduction: Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) is an autoimmune disease due to peripheral destruction but also impaired central production of platelets. Autoimmune reaction directed against megakaryocytes (MKs) has been described, and may explain morphological abnormalities of MKs observed in some patients with primary ITP. Thrombopoietin receptor agonists (TPO-RAs) are indicated as second-line treatments for ITP, but no predictive factors of response used in clinical routine practice has been demonstrated. The utility of systematic bone marrow smears (BMS) at ITP diagnosis is discussed. Howerer, it is usually recommended before second-line treatments. Two studies have suggested an association between MK abnormalities and response to corticosteroids in primary ITP, but none have investigated this association for TPO-RAs. This study aimed to investigate the association between MK abnormalities and response to TPO-RAs in adult patients with primary ITP.
Methods: The source of population was the CARMEN registry. The CARMEN (Cytopénies Auto-immunes: Registre Midi-PyréneEN) registry is aimed at the prospective follow-up of all incident ITP adults in the French Midi-Pyrénées region (South-West of France, 3 million inhabitants) since June 2013. Each investigator follows all adult patients (aged ≥18 years) with incident ITP in routine visit or hospital stay. ITP was defined by international definition (platelet count <100 x 10 9/L and exclusion of other causes of thrombocytopenia). The study population consisted in all patients included in the CARMEN registry between June 2013 and March 2018 with primary ITP, treated by TPO-RA and with a BMS before initiating TPO-RA. We excluded the patients with a number of MKs <10 MK on the BMS. Morphological abnormalities were established based on literature and defined by consensus among 3 expert cytologists (AR, JBR and VDM). All MKs present on each smear were analyzed. MKs were categorized by the presence of dysplasia (monolobed MK and/or separated nuclei and/or microMKs), and according to their stage of maturation (basophilic, granular and thrombocytogenic). All patients' medical charts were reviewed by two experts in ITP (OW and GM) to determine the response to TPO-RAs. Response was defined by a platelet count between 30 and 100 G/L with at least a doubling of basal platelet count according to the international definition. In case of subsequent exposure to both TPORAs in a single patient, response was defined by response to at least one TPO-RA in the main analysis. We performed a subgroup analysis by TPORAs.
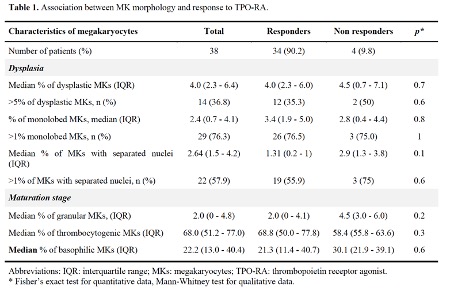
Results: During the study period, 451 patients with incident ITP were included in CARMEN-registry. Among them, 105 had been treated by TPO-RAs, including 65 with BMS before the exposure to TPORA. We then excluded 20 patients with secondary ITP and 7 with less than 10 MKs on the BMS. We finally included 38 patients in the analysis. Median age at diagnosis was 71 years (interquartile range - IQR: 31 - 94) and 34.2% were women. Thirty-three patients were treated with eltrombopag, 17 with romiplostim including 13 who were exposed to both TPORAs. Thirty-four (89.4%) achieved response. The median number of MKs analyzed per patient was 137 (IQR: 50 - 265). All results are presented in Table 1. In the main analysis, there was no significant difference in the median percentage of dysplastic MKs in responders (4.0%, 95% confidence interval - CI: 2.3 - 6.4) and non-responders (4.5%, 95% CI: 0.7 - 7.1). There was a trend for a higher proportion of granular MKs (4.5%, 95% CI: 3 - 6) and basophilic MKs (30.1%, 95% CI: 21.9 - 39.1) in non-responders comparing to responders (granular: 2.0%, 95% CI: 0 - 4.1; basophilic: 21.3%, 95% CI: 11.4 - 40.7). Results were similar in the subgroup of patients treated with eltrombopag (data not shown; the low number of patients treated with romiplostim precluded any analysis).
Conclusion: In this study, neither MK abnormalities nor the pattern of MK maturation stages were significantly associated with response to TPO-RAs. These results do not support a systematic bone marrow smear in patients with primary ITP to look for morphological predictive factors of response to TPO-RA.
Comont: AstraZeneca: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Abbvie: Honoraria, Research Funding. Moulis: Amgen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Grifols: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Sobi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Argenx: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal